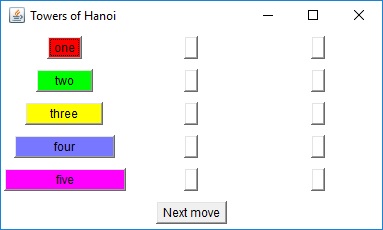
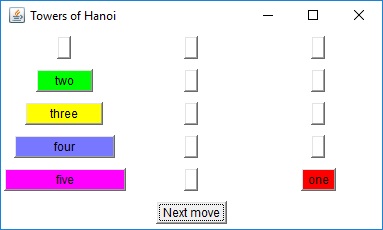
Towers of Hanoi
The classic recursive algorithm for solving this problem suggests a function with the following signature and usage.
void move( int num,
int from,
int to,
int aux ) { ... }
...
move( 5, 0, 2, 1 );
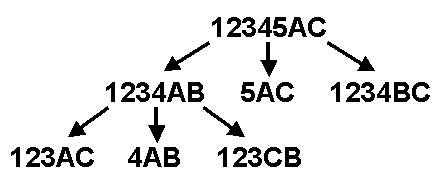
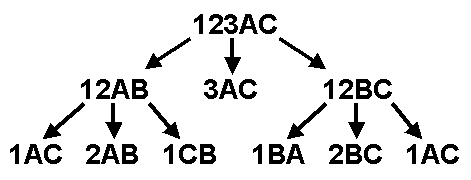
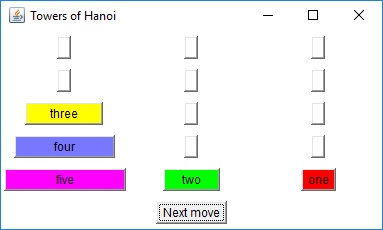
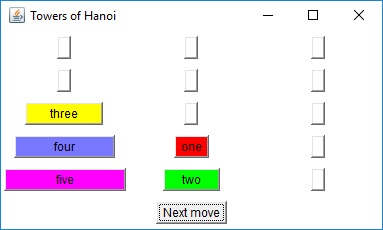
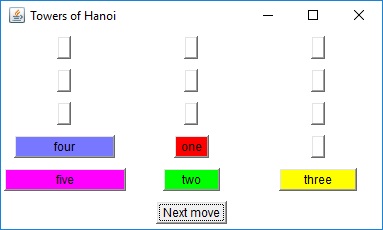
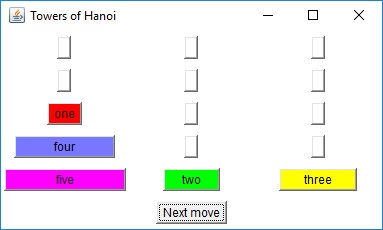
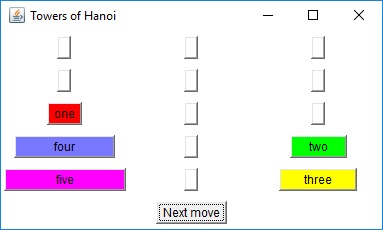
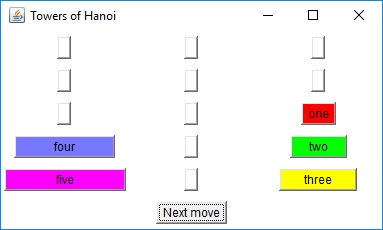
The two diagrams to the right offer graphical insight on how this
algorithm works. You start with the goal of moving disks 1 through
5 from peg A to peg C. This can be accomplished in three steps: move
the top four disks to the "aux" peg, move the largest disk to the "to"
peg, and finally move the remaining four disks from the "aux" peg to the
"to" peg.Each "composite" move is decomposed until nothing but single-disk moves are achieved. The bottom diagram is the decomposition of the lower-left step of the top diagram.